Sandbox: the testing environment for financial innovation
To help the financial sector go digital, regulators have set up testing environments or sandboxes for innovative technological solutions. A sandbox allows supervisors and project promoters to work together in a controlled setting, where both can learn and gain significant benefits.
29/10/2024
Keeping up with and adapting to the technological revolution is a challenge for both financial authorities and the financial sector. Financial innovation and digitalisation bring opportunities, but they also pose risks to the financial system and its participants that need to be properly managed. In addition, some technological solutions may not conform to existing regulations. In this setting, testing in a sandbox can be a valuable tool. Let’s explore what a sandbox is, how it works and the benefits it can provide.
A sandbox makes it possible to test technological innovations applicable to the financial system. To this end, a plan agreed with one or several competent authorities is followed in a controlled environment where risks have been minimised.
A sandbox fosters innovation in two ways: first, by helping project promoters (banks or other financial institutions, tech companies, other firms and even individuals) to verify if their initiatives comply with the regulations in force; and second, by enabling the authorities to analyse the potential effects of implementing those solutions and to identify possible improvements to the regulatory framework.
The Spanish sandbox
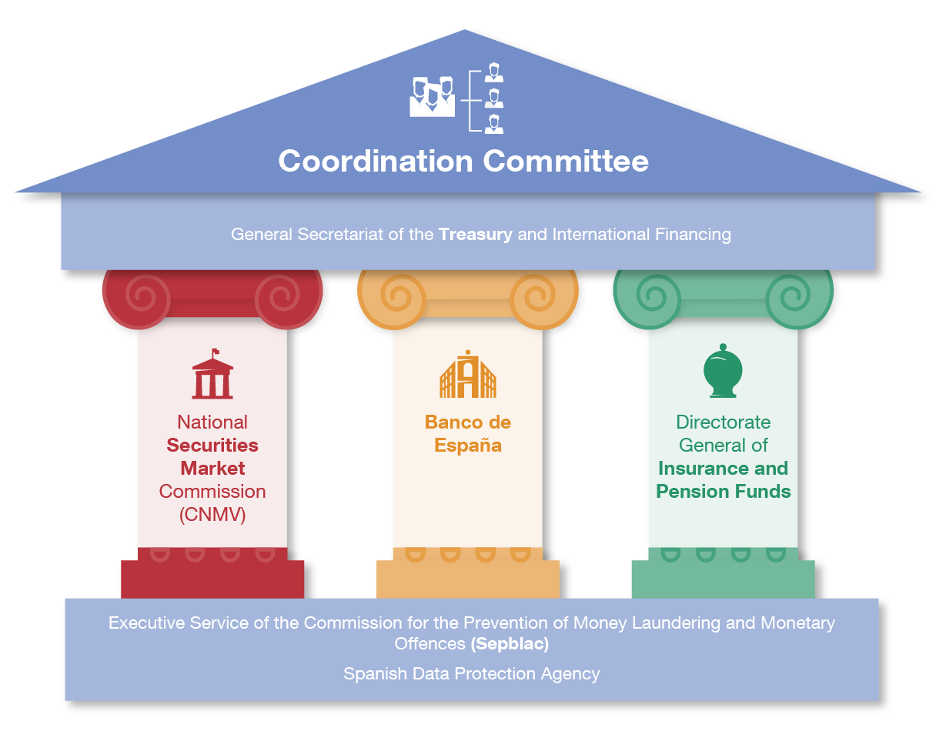
The Spanish sandbox was created in late 2020 by the Law for the digital transformation of the financial system![]() . The authorities involved are members of the Coordination Committee
. The authorities involved are members of the Coordination Committee![]() , chaired by the Ministry for the Economy’s General Secretariat of the Treasury
, chaired by the Ministry for the Economy’s General Secretariat of the Treasury![]() (see Figure 1).
(see Figure 1).
Figure 1
SANDBOX COORDINATION
SOURCE: Banco de España.
The committee members include the financial supervisors (the Banco de España, the National Securities Market Commission![]() (CNMV) and the Directorate General of Insurance and Pension Funds
(CNMV) and the Directorate General of Insurance and Pension Funds![]() and other authorities such as Sepblac
and other authorities such as Sepblac![]() . The Treasury manages the applications to the sandbox
. The Treasury manages the applications to the sandbox![]() and, depending on the characteristics of each project, assigns them to the relevant supervisory authority, which assesses them and, if the application is successful, monitors the tests.
and, depending on the characteristics of each project, assigns them to the relevant supervisory authority, which assesses them and, if the application is successful, monitors the tests.
What stages do projects go through in the sandbox?
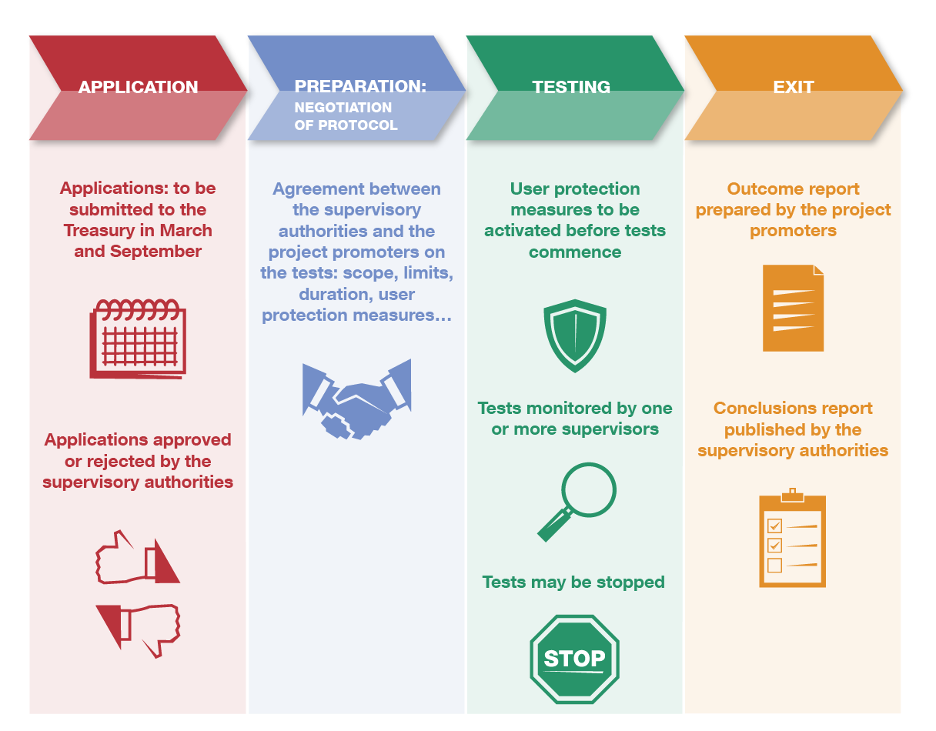
There are four phases: application, negotiation of protocol (preparation), testing and exit (see Figure 2).
Figure 2
SANDBOX STAGES
SOURCE: Fernández Zamanillo and Toloba (2024).
The sandbox makes it possible to test technological innovations for the financial system. The guidelines outline the application procedure and what participants can expect to achieve
Calls for applications![]() are announced every six months. The promoters of the selected projects must negotiate with the supervisor the rules and conditions for the pilot project and set them out in the protocol. After this, the testing phase begins. The last stage of the process is the exit phase, in which the promoter prepares a report on the test results and the authorities publish a document with their conclusions.
are announced every six months. The promoters of the selected projects must negotiate with the supervisor the rules and conditions for the pilot project and set them out in the protocol. After this, the testing phase begins. The last stage of the process is the exit phase, in which the promoter prepares a report on the test results and the authorities publish a document with their conclusions.
Specific guidelines![]() have been drawn up to explain the application procedure and what innovation promoters can expect to achieve by participating in the sandbox.
have been drawn up to explain the application procedure and what innovation promoters can expect to achieve by participating in the sandbox.
Which projects are eligible for the sandbox?
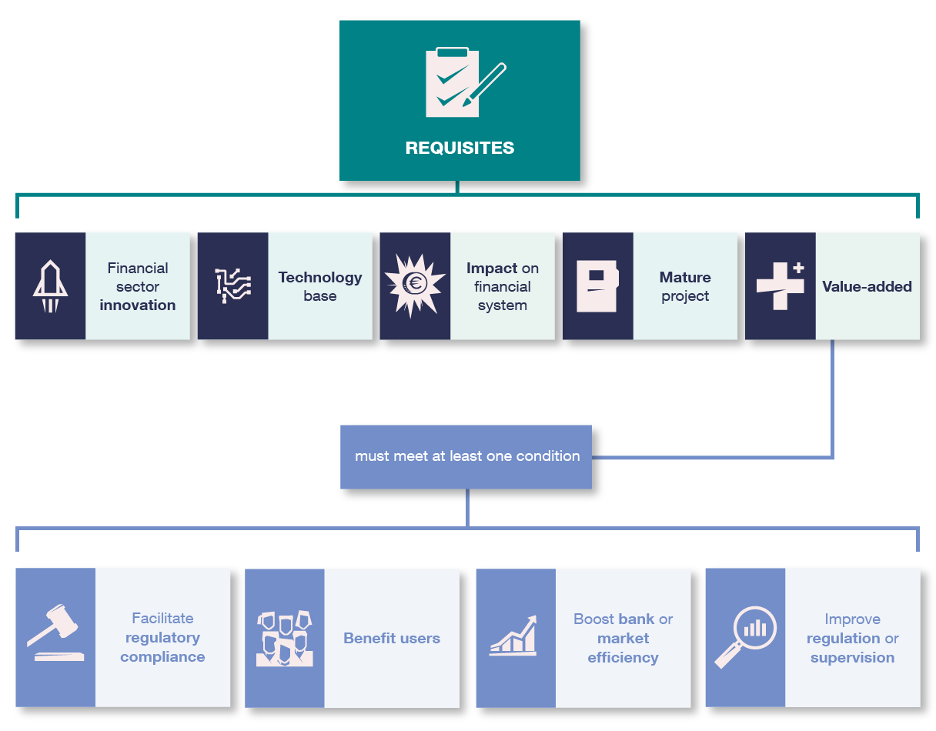
To be eligible for the regulatory sandbox, they must be technology-based innovation projects applicable to the financial system and must be sufficiently advanced to be suitable for testing. They must also offer potential utility or value-added compared with existing solutions in the areas listed in Figure 3.
Figure 3
SANDBOX ENTRY CRITERIA
SOURCE: Fernández Zamanillo and Toloba (2024).
Not all innovative projects need to pass through the sandbox, at least not directly. Indeed it is advisable for the first contact with the supervisor to be made through the queries on technology-based financial innovation![]() channel, which enables rapid and informal communication.
channel, which enables rapid and informal communication.
We advise using the technology-based financial innovation enquiry channel for rapid and informal contact with the supervisor
Innovations that pass through the sandbox include novel use cases, which may subsequently become standard practice in our financial activities. For example, new payment methods or digital identity mechanisms for customer interaction with banks.
What are the benefits of participating in the sandbox?
The experience gained so far has given the Banco de España access to a wide range of use cases. This has allowed us to reflect on the implications of implementing these initiatives and on their fit in the present and future regulatory framework.
For their part, project promoters who have passed through the sandbox have benefited from interaction with the supervisor, which has helped to streamline their processes and fine-tune their initial proposals. This experience has helped them to settle any regulatory doubts they may have had and to identify potential regulatory barriers to their projects. It has also boosted their internal and external image, making it easier for them to access financing and potential customers.
In short, the sandbox is a sign of the authorities’ commitment to financial system innovation. It has also proved very beneficial to supervisors and project promoters alike.
DISCLAIMER: The views expressed in this blog post are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily coincide with those of the Banco de España or the Eurosystem.


