Planning banking supervision: prioritising what truly matters
Banking supervision is tailored to the risks to which banks are exposed and to their vulnerabilities, ensuring that the areas of greatest concern are reviewed. Setting supervisory priorities allows for more effective supervision and more efficient management of resources.
“The essence of strategy is choosing what not to do”
Michael Porter
Banking supervision![]() seeks to ensure that the banking system remains safe and sound. In order to increase the effectiveness of its actions, every year a set of supervisory priorities is set out for the Spanish banking sector as a whole. Thanks to this information, banks know what supervisory activity will entail. But how are the supervisory priorities established? What are this year’s priorities?
seeks to ensure that the banking system remains safe and sound. In order to increase the effectiveness of its actions, every year a set of supervisory priorities is set out for the Spanish banking sector as a whole. Thanks to this information, banks know what supervisory activity will entail. But how are the supervisory priorities established? What are this year’s priorities?
How are the supervisory priorities set and what do they mean for individual banks?
The supervisory priorities for Spanish banks are set by two organisations:
- The Single Supervisory Mechanism (SSM)
 , of which the Banco de España is a member, sets the priorities for significant
, of which the Banco de España is a member, sets the priorities for significant  (i.e. the largest) euro area banks, based on the process summarised in Figure 1, and publishes
(i.e. the largest) euro area banks, based on the process summarised in Figure 1, and publishes them at the end of the year prior to their implementation.
them at the end of the year prior to their implementation. - The Banco de España sets the priorities for the remaining Spanish banks.
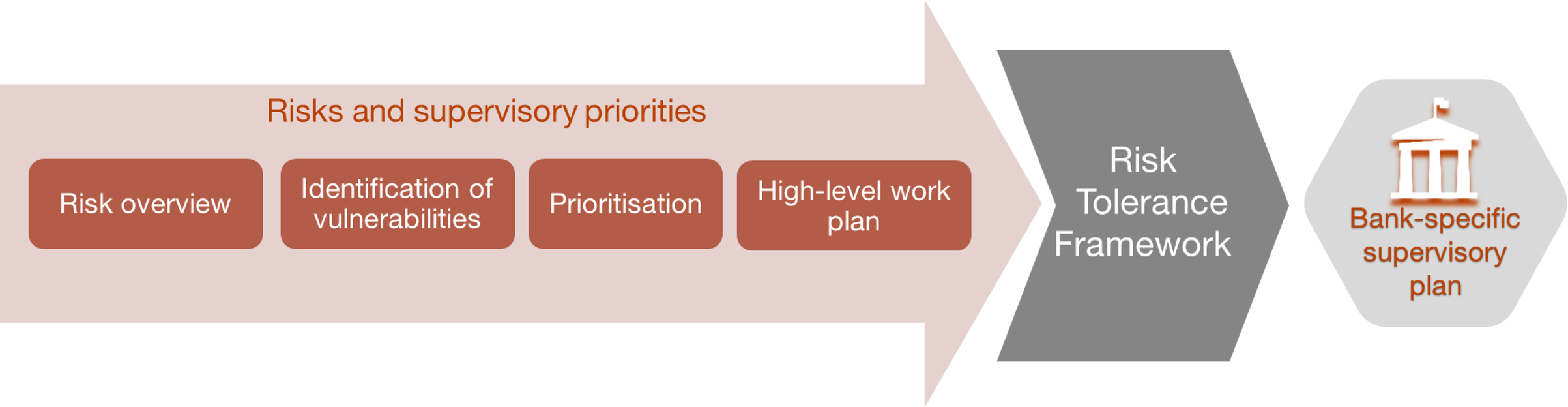
Figure 1
SSM PROCESS FOR DETERMINING RISKS AND PRIORITIES AND APPLICATION TO SIGNIFICANT BANKS
SOURCE: Banco de España.
NOTE: The Single Supervisory Mechanism (SSM)![]() is responsible for supervising significant euro area banks.
is responsible for supervising significant euro area banks.
The priorities for the two groups are detailed in our Supervision Report![]() , which is published in the first months of each year.
, which is published in the first months of each year.
The SSM sets the supervisory priorities for significant banks and the Banco de España covers the rest
The process begins with an assessment of the risks affecting the banking sector. This analysis is used to identify credit institutions’ vulnerabilities and prioritise the most important ones, and a work plan is then drawn up.
Macroeconomic, financial and geopolitical considerations are taken into account, as are market perceptions and the findings of supervisory reviews.
How do the supervisory priorities affect the supervision of individual banks? Not all priorities are automatically applied to all banks. The supervisory team decides which ones to address on a case-by-case basis. To do so, the SSM uses a tool called the Risk Tolerance Framework![]() .
.
This tool combines top-down guidance issued by the Supervisory Board on prioritised risks and vulnerabilities with bottom-up relevance assessments for each individual bank. This combined approach makes it possible to tailor the supervisory activities to each institution.
What issues have influenced the supervisory priorities in recent years?
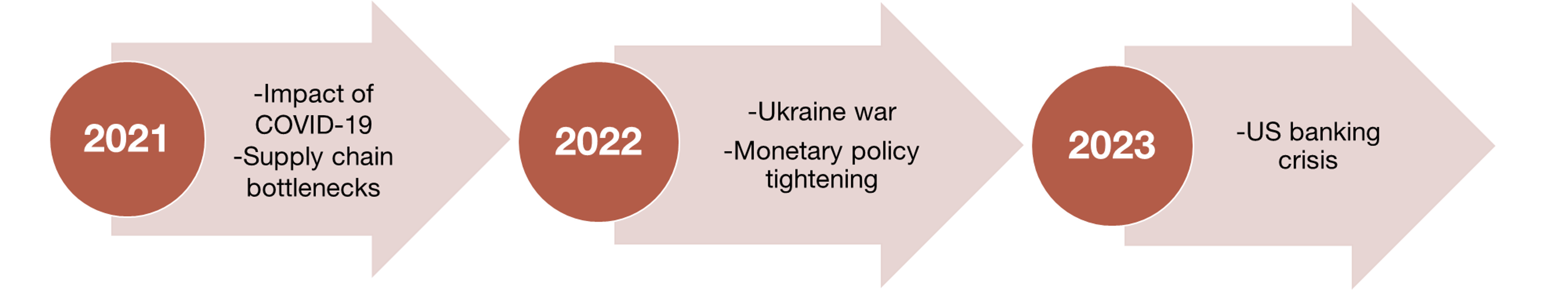
The past few years have been marked by a series of economic, financial and geopolitical shocks (see Figure 2). This sequence of events has brought home the need to strengthen the financial sector’s resilience to unexpected shocks.
Figure 2
KEY MACRO-FINANCIAL AND GEOPOLITICAL EVENTS 2021-2023
SOURCE: Banco de España.
For example, in 2021, uncertainty about how the pandemic would pan out, along with problems in supply chains, heightened concerns about an increase in bankruptcies and non-performing loans. In 2022, the war in Ukraine sent inflation soaring, requiring a tightening of monetary policy for the first time in years. This redefined supervisory needs:
- Banks’ ability to correctly identify and assess credit risk was revised. Initially, the focus was on heavily indebted firms that were vulnerable to the pandemic. Attention then turned to the sectors hit by rising energy prices, supply chain disruptions and higher interest rates.
- Maximum prudence was called for in terms of provisions and capital.
- Emphasis was placed on diversifying banks’ funding sources to fortify them against potential market disruptions and on reviewing the strategies for repaying the funding received from the European Central Bank.
Last year, the banking crisis![]() that originated in the United States showed just how important liquidity and interest rate risks can be. Although the euro area escaped largely unscathed, supervisors turned their attention to stepping up preparations in anticipation of liquidity shocks and the need to manage interest rates.
that originated in the United States showed just how important liquidity and interest rate risks can be. Although the euro area escaped largely unscathed, supervisors turned their attention to stepping up preparations in anticipation of liquidity shocks and the need to manage interest rates.
Meanwhile, the banking sector is grappling with structural trends that are profoundly reshaping the risks it faces. Supervisors must adapt accordingly.
- The digital transformation of the financial sector has prompted banks to review their strategies, with the aim of making their business models more sustainable.
- Technological risk has gained prominence in recent years. This is due to the increasing digitalisation of processes, more widespread outsourcing of certain essential services and the rise in cyber incidents.
- Climate risk affects everything, and the banking sector is no exception. Banks must ensure that their strategy and management duly take account of climate-related and environmental physical and transition risks.
Lastly, governance has become a regular feature of the supervisory priorities in recent years, testifying to its growing importance as a means of ensuring that banks are soundly managed.
Banking supervision must adapt to structural changes such as digital transformation and technological and climate risks
What are the supervisory priorities for 2024?
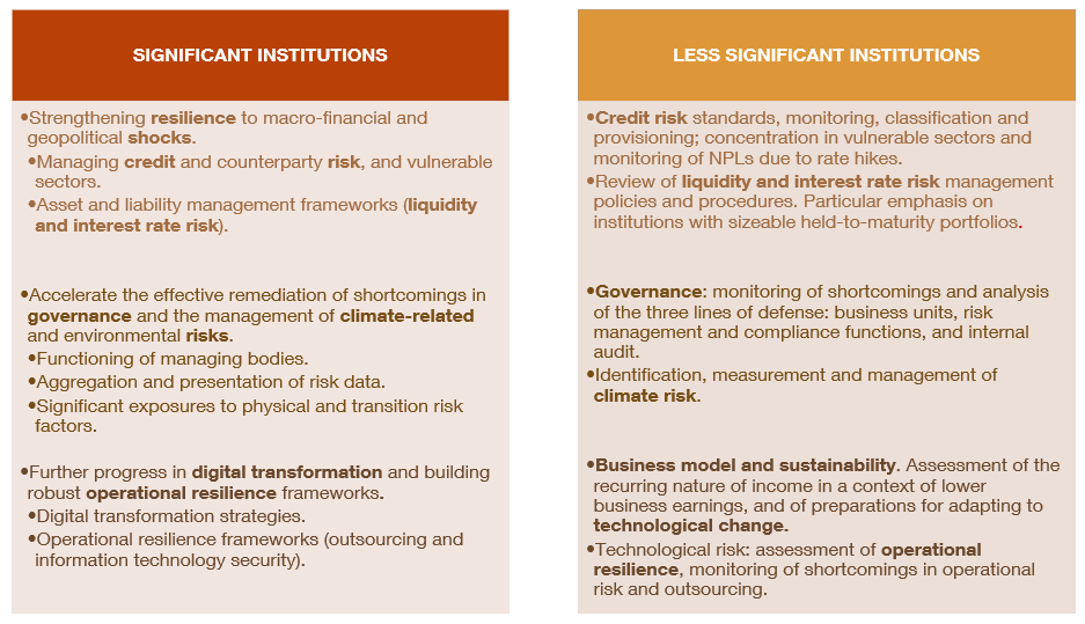
Figure 3 shows the supervisory priorities guiding the Banco de España's supervisory activities this year. It draws a distinction between significant institutions, whose priorities have been set for the period 2024-2026, and less significant institutions, with priorities for 2024. These priorities reflect the aspects described above, and have been gradually adjusted as risks have changed.
Figure 3
SUPERVISORY PRIORITIES FOR 2024
SOURCE: Banco de España.
In short, given the challenges facing the banking sector and the way such challenges evolve, the strategic direction provided by this Risks and Priorities process is essential to ensuring that supervisors can effectively address the sector’s risks and vulnerabilities.
DISCLAIMER: The views expressed in this blog post are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily coincide with those of the Banco de España or the Eurosystem.

